Our Technology
Modular Production
Innovation That Drives Efficiency
Alpha Motor is advancing vehicle manufacturing efficiency, making EVs more accessible. We focus on electrifying trucks — the largest addressable vehicle market in the U.S. Leveraging modular production technology, we’re making EVs more affordable, reliable, and scalable, key factors driving growth.
Our manufacturing efficiency reduces complexity and simplifies assembly, providing the flexibility to produce EVs sized for optimal performance.
-
Modular vehicle technology is producing vehicles from standardized parts that can be easily interchanged or assembled, making manufacturing efficient, flexible, and scalable.
-
Standardizing Components: Simplifies inventory and reduces the variety of parts required.
Reducing Production Time: Pre-designed modules shorten assembly processes.
Improving Scalability: Easier expansion or adjustment of production lines to meet demand.
Facilitating Maintenance: Interchangeable parts lower maintenance time and costs.
Enabling Customization: Rapidly adapting standardized modules to different applications without extensive redesign.
-
Modular vehicle technology is driven by digitalizing manufacturing, enabling virtual validation of modular parts, accelerating optimization and directly reducing production costs.
Reducing production costs: Lower costs from optimized manufacturing lower the price for consumers.
Enabling customization: Flexible, modular parts allow tailored vehicles for diverse market needs and price ranges.
Shortening development cycles: Virtual validation accelerates EV production, getting vehicles to market quicker.
Simplifying maintenance: Standardized modular components reduce repair and ownership expenses.
Scaling production: Digital modular manufacturing easily meets growing demand, increasing availability.
Modular Automotive Production Technology
Flexible, Scalable System
Efficient EV Production
Created by Industry Experts
Through patented Modular Automotive Production technology, Alpha Motor enhances flexible assembly, quality standardization, and manufacturing efficiency to deliver a diverse range of models. From technical efficiencies and process optimization to real-world consumer benefits, our innovation is guided by three core principles: Value, Variety, and Versatility.
-
Open System: Enables component compatibility across different models and scalable production.
Vehicles are manufactured using interchangeable, standardized components.
Efficient manufacturing at different scales without significant changes to processes.
Standardized process used across multiple vehicle models, streamlining production.
Our open system makes it easier to produce different types of vehicles efficiently. You can scale production up or down based on demand and share parts across different models, saving time, costs, and resources.
-
Modular Production: Boosts scalability and variety through optimized processes, driving economies of scale.
Modular production makes it easier to manufacture more vehicles and different models quickly, helping lower costs and keeping the supply chain strong even when demand changes.
-
Customization: Unlocks a range of price options to address various needs while simplifying customization and after-sales service.
Our customization allows vehicles to be tailored to different price ranges and customer preferences, while keeping service and maintenance simple.
-
Our technology focuses on these key priorities for long-term growth:
Market Fit
Compliance
Unit Economics
Manufacturing Scalability
After-Sales
-
Overview
Raw Material Sourcing & Processing
Component Manufacturing
Chassis & Body Construction
Powertrain & Drivetrain Integration
Interior Assembly & Electronics
Final Vehicle Assembly & Calibration
Quality Control & Testing
Final Inspection & Delivery
1. Raw Material Sourcing & Processing
Extraction, refinement, and preparation of raw materials for manufacturing.Battery Materials; Structural & Body Materials; Motor & Electronics; Plastics & Composites; Glass & Rubber
2. Component Manufacturing & Preassembly
Conversion of raw materials into functional vehicle components, with preassembly of modular subsystems.Battery Pack
Electric Motor
Chassis & Body Panel Formation
Electrical & Control Components
Lighting & Safety Systems
HVAC & Thermal Systems
3. Chassis & Body Construction & Painting
Fabrication and assembly of the structural frame and exterior body panels.Chassis & Frame Integration
Body Panel Installation
Painting & Coating
Crash Structure & Safety Cell Construction
Seals, Insulation, and Coatings Applied
4. Powertrain & Drivetrain Integration
Installation of propulsion, energy storage, and drivetrain systems.Battery Pack Installation
Electric Motor & Transmission Mounting
Suspension & Axle Assembly
Power Electronics & Charging System Installation
5. Interior Assembly & Electronics
Installation of interior components and electronic systems.Seats, Dashboard, and Center Console Installed
Infotainment System Mounted
HVAC System Installed
Wiring Harness & Sensors Connected
Safety Features Installed
Lighting System Installed
6. Final Vehicle Assembly & Calibration
System alignment, calibration, and operational verification.Brake System Testing & Adjustment
Charging System Validation
Software Deployment & Updates
Driver Assistance System Calibration
7. Quality Control & Testing
Validation of vehicle performance, safety, and compliance.Battery Performance Testing
Powertrain & Acceleration Validation
Braking & Safety System Testing
Infotainment System Verification
Interior Fit & Finish Inspection
8. Final Inspection, Customization & Delivery
Completion of final quality checks, customer-specific configurations, and logistics.Surface Finish & Aesthetic Inspection
Customer Specification Adjustments
Logistics & Delivery
-
Powertrain
1. Battery Pack
2. Battery Management System (BMS)
3. Electric Motor
4. Inverter
5. DC-DC Converter
6. Onboard Charger (OBC)
7. E-Axle (Gearbox)
8. Vehicle Control Unit (VCU)Energy & Charging
9. Charging Port Assembly
10. Charging Control Unit
11. High-Voltage Wiring Harnesses
12. High-Voltage ConnectorsThermal & Environmental Systems
13. Thermal Management System
14. Battery Cooling System
15. Heat Pump
16. HVAC SystemChassis & Safety
17. Brake System (regenerative and mechanical)
18. Suspension System
19. Steering System (EPS units)
20. Airbag System
21. Electronic Stability Control (ESC)
22. ABS/ESC Control UnitsControl & Electronics
23. Controller / ECU
24. Body Control Module (BCM)
25. Gateway Module
26. Telematics Control Unit (TCU)
27. Centralized Computing Units (Domain Controllers)ADAS & Autonomy
28. Cameras
29. Radar Sensors
30. LiDAR Sensors
31. Ultrasonic Sensors
32. ADAS ECUs (Processing Units)User Interface & Connectivity
33. Infotainment System
34. Instrument Cluster
35. Head-Up Display (HUD)
36. Human-Machine Interface (HMI)
37. Telematics & Connectivity Modules (5G, V2X, GPS)Lighting & Exterior Systems
38. Headlamps (LED)
39. Taillights
40. Daytime Running Lights (DRL)
41. Interior Lighting Modules*Not exhaustive.
-
1. Battery Management System (BMS)
Monitors and controls battery voltage, current, temperature, and charging status.
Ensures battery efficiency, safety, and extends battery lifespan.
2. Power Electronics
Inverter Systems: Convert DC from batteries to AC for the motor; control motor speed and torque.
DC-DC Converters: Regulate voltage levels between battery pack and vehicle electronics.
3. Electric Motor Control
Semiconductors manage motor operation, controlling torque, power distribution, efficiency, and regenerative braking functions.
4. Charging Systems
Manage AC/DC conversion during vehicle charging.
Control charging speed and protect the battery from voltage fluctuations.
5. Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS)
Radar, LiDAR, and camera processing chips for collision avoidance, lane keeping, and autonomous driving features.
6. Vehicle Control Units (VCUs) and Sensors
Process data from sensors throughout the vehicle.
Enable software-driven vehicle control, monitoring, diagnostics, and connectivity.
7. Infotainment and Connectivity
Power multimedia, navigation systems, display screens, voice control, and internet connectivity.
8. Thermal Management Systems
Control heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems for battery cooling and passenger comfort.
-
Metals
Steel – Body panels, chassis, structural supports, motor housing
Aluminum – Body structure, motor casing, battery enclosures, cooling plates
Copper – Wiring, busbars, motor windings, inverters, charging ports
Brass – Electrical connectors and terminals
Magnesium – Lightweight structural parts, transmission casings
Zinc – Plating, die-cast parts
Titanium – High-strength fasteners, specialty suspension parts
Rare Earth Elements
Neodymium – Permanent magnets in traction motors
Dysprosium – Added to neodymium for high-temperature stability in magnets
Terbium – Used in high-performance magnet alloys
Lanthanum – Battery chemistries (nickel-metal hydride)
Praseodymium – Magnet alloys
Battery Materials
Lithium – Core material in lithium-ion batteries
Nickel – Cathode material for high energy density
Cobalt – Cathode material for thermal stability
Manganese – Cathode material (NMC chemistry)
Graphite – Anode material
Silicon – Emerging anode material (used in blends with graphite)
Aluminum (battery use) – Cathode current collectors
Copper (battery use) – Anode current collectors
Electrolytes – Organic carbonates and lithium salts
Separators – Polyolefin-based microporous membranes
Advanced Semiconductors
Silicon – Traditional semiconductor for inverters and control electronics
Silicon Carbide (SiC) – Power electronics for inverters and high-voltage systems
Gallium Nitride (GaN) – High-efficiency onboard chargers, DC-DC converters
Germanium – Used in high-speed electronics and sensors
Plastics & Polymers
Polypropylene – Battery casing, interior parts
Polycarbonate – Headlamp lenses, electronics housings
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) – Interior panels, dashboards
Nylon (PA6/PA66) – Under-the-hood components, connectors
Polyurethane – Foam insulation, seats, seals
Epoxy Resins – Adhesives, composite matrix materials
Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE) – Cable insulation, weather seals
Composites & Other Structural Materials
Carbon Fiber – Lightweight body panels, structural reinforcements (premium EVs)
Glass Fiber Composites – Reinforced panels and housings
Natural Fiber Composites – Door panels, linings (flax, hemp, kenaf)
Glass – Windows, displays, headlamps
Foams & Insulation – Acoustic and thermal management materials
Chemicals & Fluids
Coolants (glycol-based) – Battery and power electronics thermal management
Lubricants – Transmission, e-motor, and chassis components
Adhesives & Sealants – Structural bonding, battery pack sealing
Paints & Coatings – Corrosion protection and aesthetics
Rubber & Elastomers
Synthetic Rubber – Tires, weather stripping, bushings
Silicone Rubber – High-voltage insulation, gaskets
Butyl Rubber – Vibration isolation, sealing
*Not exhaustive.
-
Our automotive expertise and passion drive our commitment to advancing transportation. Below are the key reasons why trucks are set to lead the energy transition in the industry.
Largest Addressable Market – Trucks are the best-selling category in the U.S., representing a significant portion of the market
Better Business Opportunity – Trucks have strong unit economics, enabling greater capital efficiency.
Strong Consumer Demand – Trucks have high usage rates, creating a strong entry point for EV adoption.
Scalability – Trucks align perfectly with our modular technology, streamlining production while enabling options.
Tax Incentives – Federal and state programs offer tax credits and rebates for buying electric trucks.
Emissions Impact – Gas-powered trucks burn more fuel, so switching to electric reduces emissions significantly.
EV Performance – EV technology enhances truck capabilities, delivering greater performance and value to consumers.
Growing Market – Electric trucks are set for major growth, with sales expected to rise over 34% annually by 2030.
-
Alpha Motor’s electric vehicles are designed, engineered, and manufactured in the United States.
-
*Sources: goodcarbadcar.net, irs.gov, psmarketresearch.com, marketsandmarkets.com
Our Performance Advantages
Optimization and Scalability
How our technology optimizes EV performance.
-
Modular Platform Architecture maximizes central battery placement, improving range and driving dynamics.
This supports longer trips with fewer charging stops and provides a more balanced, responsive driving experience.
-
Modular Powertrain System supports multi-motor configurations, delivering powerful acceleration and high towing capacity.
This ensures strong performance for both daily driving and heavy-duty tasks.
-
Modular Suspension System combines independent suspension with shock absorption to maintain comfort and control across various terrains.
This provides a smoother, more stable ride whether on highways or rugged roads.
-
Modular Energy Systems enable uniform energy management across different vehicles, ensuring optimal range, efficiency, and reliability.
This reduces electronic complexity and improves production efficiency across the lineup.
-
Modular Production System standardizes components and manufacturing processes, boosting production efficiency and scalability.
This enables cost-effective manufacturing while maintaining consistent quality and performance.
-
Below are other areas of development where we advance EV performance:
1. Powertrain System
Maximize Power Density and Efficiency: Deliver strong power output with compact motors to optimize space and energy use.
Enhance Energy Transfer: Improve power conversion efficiency, reducing energy losses during acceleration and braking.
Optimize Power Delivery: Simplify gear configurations for smoother performance and maximum efficiency.
Improve Power Distribution: Utilize high-voltage architecture to reduce resistive losses and boost performance.
Balance Performance and Efficiency: Adapt power output dynamically to meet varying driving conditions.
2. Energy Storage System
Extend Driving Range: Maximize energy capacity with high-density battery packs in compact structures.
Optimize Battery Performance: Regulate charging, discharging, and thermal conditions for longevity and efficiency.
Reduce Energy Losses: Minimize heat generation through low-resistance battery architecture.
Improve Charging Efficiency: Distribute power dynamically across battery modules for faster charging.
Minimize Battery Degradation: Adapt charging strategies based on usage patterns to preserve battery health.
Ensure Consistent Charging Performance: Maintain ideal battery temperatures for efficient charging in all climates.
3. Thermal Management System
Improve Thermal Efficiency: Enhance climate control to reduce energy use in extreme conditions.
Maintain Optimal Temperatures: Actively regulate battery and motor temperatures for peak performance.
Balance Thermal Load: Integrate cooling and heating systems for both powertrain and cabin comfort.
4. Energy Efficiency and Recovery
Optimize Energy Consumption: Use real-time data to forecast and manage energy use effectively.
Maximize Energy Recovery: Improve regenerative braking systems to extend driving range.
Enhance Braking Efficiency: Adjust regenerative braking intensity to optimize energy recovery.
Simplify Driving for Efficiency: Use one-pedal driving to recover energy seamlessly during deceleration.
5. Aerodynamics and Lightweight Structures
Reduce Aerodynamic Drag: Develop streamlined vehicle forms to enhance efficiency, especially at high speeds.
Minimize Air Resistance: Optimize surface contours to reduce turbulence and improve aerodynamic flow.
Lower Vehicle Weight: Use lightweight materials to decrease mass without compromising safety or durability.
Simplify Structural Components: Integrate structural parts to reduce weight and enhance manufacturing efficiency.
6. Charging System
Optimize Charging Efficiency: Adjust charging speeds dynamically to balance energy efficiency and battery health.
Improve Charging Throughput: Enhance power distribution at charging stations to reduce wait times.
Ensure Fast and Reliable Charging: Use advanced control systems to maintain battery durability during fast charging.
7. Vehicle Intelligence & Software Systems
Continuously Improve Vehicle Performance: Deliver over-the-air updates for software enhancements without hardware changes.
Optimize System Performance: Leverage real-time data to enhance energy management and driving dynamics.
Ensure Consistent Performance: Deploy software updates adaptively based on vehicle usage patterns.
8. Navigation and Driver Assistance Systems
Optimize Route Efficiency: Plan travel routes based on energy consumption, traffic, and charging availability.
Reduce Travel Time: Adjust routes dynamically to avoid congestion and improve efficiency.
Enhance Situational Awareness: Use real-time environmental data for improved driving safety.
Adapt to Road Conditions: Continuously recalculate driving paths to respond to changing conditions.
Improve Driver Safety: Predict road user behavior to enhance response times and reduce risks.
Reduce Energy Consumption: Optimize cabin systems and electronics for minimal energy draw.
Our Key Enablers
Unlocking Scalable Efficiencies
How our technology optimizes EV production.
-
Our modular technology is based on an open platform with interchangeable parts, enabling manufacturing flexibility.
Our modular platform’s adaptable structure enables vehicle production of different sizes and purposes using shared components and processes.
Strategic decoupling of components enhances adaptability, allowing optimized EV technology to integrate across a diverse range of models.
Process optimization streamlines production, driving economies of scale while simplifying maintenance and repairs.
-
EV Cost Distribution (% of Total Cost)
Battery Pack: 35%
Electric Motor: 15%
Power Electronics: 10%
Vehicle Body: 15%
Interior Components: 10%
Chassis & Suspension: 5%
Thermal Management System: 3%
Other Electronics & Software: 5%
Assembly & Labor: 1%
Miscellaneous (Paint, Lighting, etc.): 1%
*Percentages represent estimated share of total vehicle cost.
-
Alpha Motor’s “High Impact Standardization” focuses on strategically standardizing components and manufacturing processes across multiple vehicle models to streamline high-quality production.
Standardizing key vehicle systems drives automation, accelerates time to market, and simplifies after-sales service.
Our approach enhances operational efficiency and drives economies of scale through streamlined production, enabling competitive pricing.
Definition:
High Impact Standardization: Strategic product engineering and process optimization that streamline high-quality production and drive scalability.
Standardization Impact:
Core Components (90-100% Standardization): The battery pack, electric motor, power electronics, chassis, and suspension offer the highest potential for near-total standardization.
Supporting Systems (60–80% Standardization): Thermal management, electrical architecture, infotainment, and interior components can be standardized based on vehicle model or size.
Exterior Components (30–50% Standardization): Standardization focuses on lighting, mirrors, underbody panels, glass, door handles, seals, roof rails, and structural elements—balancing cost savings with design flexibility for model-specific features.
Projected Total Savings (20% Reduction): Achieved through standardizing key mechanical, electrical, and exterior components, alongside optimized production processes and supply chains for greater efficiency.
-
High Impact Standardization (Component Breakdown):
Battery Pack
Battery Cells: Standardizing the type of battery cells (e.g., lithium-ion) across multiple models.
Battery Modules: Using common battery modules, with variations in total pack size depending on the vehicle.
Electric Motor
Motor: A standardized electric motor, with adjustments to power output for different vehicle models.
Inverter: Standardized power electronics to control the motor, used across all models.
Power Electronics
Inverter and Converter: Shared power conversion systems (e.g., AC to DC) for use across multiple models.
Charging System: Standardized charging ports and on-board chargers, compatible with fast-charging systems.
Vehicle Platform, Chassis & Suspension
Chassis (Modular Platform): A common chassis adaptable to different vehicle sizes (e.g., truck, SUV, crossover) using the same structural base.
Suspension: Standardized suspension components (e.g., control arms, struts), with adjustments for ride heights or load capacities.
Thermal Management System
Cooling Systems: Standardized thermal management for the battery, motor, and power electronics, with minor adjustments for different vehicle sizes or performance needs.
Electrical Architecture
Wiring Harness: A shared electrical wiring architecture used across multiple vehicle models.
Control Modules: Standardized control units (e.g., body control modules, battery management systems) to manage essential functions.
Infotainment and Software
Infotainment Systems: Standardized infotainment hardware and software across models.
Driver Assistance Systems: Standardizing cameras, sensors, and software for ADAS features like lane-keeping and adaptive cruise control.
Interior Components, Seats, HVAC
Seats (Frames and Mechanisms): Standardized seat frames and mechanisms (e.g., adjustable tracks), while materials and finishes may vary.
HVAC Systems: Shared heating, ventilation, and air conditioning units, with adjustments based on cabin size.
Steering and Braking Systems
Steering Components: Standardized steering racks, columns, and electric power steering systems across models.
Braking Systems: Standardized brake systems, including calipers, rotors, and electronic braking modules.
Safety Systems
Airbags and Restraints: Standardized airbags, seatbelts, and electronic safety control units.
Crash Structure: Standardized safety cell and crumple zones with slight variations for different vehicle types.
Exterior Parts, Lighting, Mirrors
Lighting (Headlights, Tail Lights): Standardized lighting components with minor adjustments for different body styles.
Mirrors: Common exterior mirrors.
Paint and Coating
Exterior Finishes: Standardized paint and coating processes, with variations in color options.
Production and Assembly Processes
Assembly Techniques: Standardized manufacturing processes and assembly line configurations to build multiple vehicle types with minimal changes to tooling and machinery.
-
Alpha Motor’s production operates on three key principles—modularity, standardization, and automation—to ensure efficient and scalable production.
Modularity: Built for Flexibility
Preassembled Component Integration: Key systems are preassembled, streamlining vehicle assembly.
Adaptable Assembly Lines: Different models are produced on the same line with flexible integration of modular components.
Standardization: Efficient Quality Control
Uniform Processes Across Models: Standardized tools and machines ensure consistent quality, reduce costs, and support part interchangeability.
Component Integration: Standardized part specifications streamline assembly and improve production efficiency.
Automation: Faster, Smarter Production
Automation in Key Processes: Automated systems handle repetitive tasks like forming, bonding, and painting with precision and speed.
Automated Quality Control: Automated inspections ensure consistency and precision throughout production.
Smart Manufacturing Systems: Robotics streamline repetitive tasks and reduce manual labor.
Key Benefits:
Modularity allows production flexibility.
Standardization ensures consistent quality and accelerates production.
Automation boosts production efficiency, making operations more competitive and cost-effective.
-
Standardized optimization across a diverse vehicle lineup improves unit economics and manufacturing efficiency.
Stronger unit economics, resulting from standardized optimization, enable streamlined production and cost-effective scaling.
Efficient scalability drives economies of scale, increasing product variety and enabling a range of price options to fit various needs.
-
Lower maintenance costs result from interchangeable parts and standardized assemblies.
Reducing costly redesigns accelerates time to market for future models.
Standardized parts and reduced complexity simplify service and repairs, extend vehicle lifespan, and help maintain higher resale value over time.
-
Optimizes performance across a diverse vehicle lineup while minimizing the need for highly customized solutions.
Allows for customization flexibility, enhancing performance and consumer satisfaction without requiring a complete production overhaul.
Offering a range of options enables consumers to balance cost, range, and performance.
-
Enables flexible manufacturing of multiple vehicle configurations, unlike competitors restricted to single-model production lines.
Supports cross-compatibility of parts across different models, improving costs and manufacturing efficiency.
Drives economies of scale, reduces reliance on a single product, and strengthens resilience across the entire value chain.
-
If applied incorrectly, modularity can introduce unnecessary complexity. This is why it requires deep automotive expertise guided by market demand to unlock its full potential.
At Alpha Motor, modular technology is a holistic system of manufacturing solutions that drives flexibility and optimization across the entire value chain. The key benefits include:
Improved Unit Economics: Optimizes material science for cost-efficient production while simplifying assembly and disassembly to streamline maintenance, repairs, and customization. This forms the foundation of modular efficiency by reducing production costs and enhancing operational flexibility.
Open Compatibility: Enhances component interchangeability, strengthening supply chain resilience and reducing dependency on highly customized solutions. This allows for streamlined assembly and better cost control across production cycles.
Flexible Production Lines: Maximizes output by enabling the production of multiple vehicle models on the same streamlined system, eliminating the limitations of single-model production lines. This flexibility reduces operational bottlenecks and improves capacity utilization.
Efficient Scalability: Enables rapid production scaling without increasing complexity, providing a direct and accelerated path to achieving economies of scale, which further reduces per-unit costs as production volume grows.
Diverse Lineup: Offers a wide range of solutions and configurations, allowing consumers to select options that meet their specific needs while maintaining production efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
In summary, modularity is all about how it’s applied. When implemented correctly, it transforms manufacturing into an efficient, scalable, and resilient system.
-
Consumers – Gain access to a range of models and price options with simplified maintenance and repairs, lowering the lifetime cost of ownership.
Industry – Achieves greater capital efficiency while accelerating the transition to EVs and significantly reducing carbon emissions.
Humanity – Moves toward a renewable energy ecosystem, creating a more resilient and sustainable world.
Wolf Truck Lineup
Purpose-built Pack Of Solutions
Versatile, Efficient, Powerful
Wolf Specifications
-
Origin: U.S.
Price Range: $46,000 – $52,000
Motor Options: Single, Dual Motor
Range: 250–300 miles
Towing Capacity: 3,500–5,000 lbs
Horsepower: 200–268 HP
Vehicle Size: Mid-size
Passenger Capacity: 2–3 passengers
Dimensions (L x W x H): 4,828 mm x 1,910 mm x 1,798 mm
Truck Bed Size (L x W): 6.0 ft x 4.2 ft
Customization: High Customization, Traditional Design
Off-road Capability: Good, Traditional All-terrain Design
Unique Points: High Efficiency and Versatility, Traditional Truck Layout
-
Origin: U.S.
Price Range: $52,000 – $58,000
Motor Options: Dual Motor
Range: 300–350 miles
Towing Capacity: 5,000–7,000 lbs
Horsepower: 268–335 HP
Vehicle Size: Mid-size
Passenger Capacity: 4–5 passengers
Dimensions (L x W x H): 5,355 mm x 1,950 mm x 1,828 mm
Truck Bed Size (L x W): 6.0 ft x 4.2 ft
Customization: High Customization, Traditional Design
Off-road Capability: Good, Traditional All-terrain Design
Unique Points: Extended Cabin, Traditional Truck Layout
-
Origin: U.S.
Price Range: $58,000 – $68,000
Motor Options: Dual Motor
Range: 350–400 miles
Towing Capacity: 7,000–8,500 lbs
Horsepower: 335–469 HP
Vehicle Size: Full-size
Passenger Capacity: 5–6 passengers
Dimensions (L x W x H): 5,658 mm x 1,990 mm x 1,900 mm
Truck Bed Size (L x W): 6.0 ft x 4.2 ft
Customization: High Customization, Traditional Design
Off-road Capability: Good, Traditional All-terrain Design
Unique Points: Traditional Full-size Truck Layout, High Performance
*Specifications are estimates provided for illustrative purposes only and are subject to change without notice. Actual features, performance, and pricing may vary.
Wolf Truck Variants
Wolf vs. Others
Value, Variety, Versatility
The Wolf is a versatile EV for daily driving, off-road adventures, and use as a work truck. From basic EVs to serious power, Alpha Motor offers value for everyone. 90.6% rate the Wolf as satisfactory or excellent in terms of performance.*
*As of February 2025, the survey measures consumer satisfaction based on projected vehicle price and specifications.
Our Technology Resilience
Flexible, Efficient, Scalable
Our technology reduces complexity to adapt, scale, and create lasting value.
-
Through modular production technology, components are interchangeable across models, simplifying assembly, standardizing processes, and enhancing adaptability to disruptions.
-
Our standardization of quality streamlines production, optimizes resource use, and fosters continuous improvement.
-
Our modular design, open compatibility, and standardized assemblies enhance supply chain resilience by reducing dependence on highly customized parts, which strengthens production continuity in dynamic environments.
-
Standardization and streamlined production accelerate economies of scale, improving capital efficiency. This approach supports agile operations and ensures cost-effectiveness in evolving market conditions.
-
Through process optimization and digital solutions, our technology promotes sustainability by reducing material waste and energy consumption. Standardized parts shared across models lower environmental impact and improve resource efficiency.
-
Alpha Motor’s modular platform enables flexible customization without added complexity, allowing us to meet diverse consumer needs while maintaining streamlined, efficient production.
Our Engineering Principles
Driving EV Optimization
We’re dedicated to accelerating the transition to electric vehicles.
-
Our engineering principles prioritize EV optimization. The tipping points for electric vehicle (EV) efficiency are tied to how vehicle weight and battery capacity affect energy consumption. As vehicle weight and battery capacity increase, the energy required to move the vehicle increases disproportionately, resulting in diminished efficiency.
-
As weight and battery size increase:
Acceleration: Heavier vehicles, despite having high power, generally have slower acceleration due to lower power-to-weight ratios.
Handling: Heavier vehicles have more inertia, which affects braking and cornering performance, even if they have powerful motors.
In contrast, lighter vehicles can maintain strong power-to-weight ratios and efficient power delivery, offering both strong performance and high efficiency without the need for oversized motors or battery packs.
-
Energy consumption in vehicles is roughly proportional to the vehicle’s mass. As the weight of the vehicle increases, the energy required to accelerate and maintain speed also increases.
-
Battery capacity (measured in kWh) dictates how much energy is available to supply the electric motor over time. However, the capacity of the battery does not directly determine the power output—that is more related to the powertrain design and motor size. But the relationship between battery capacity and vehicle weight can indirectly affect power delivery.
-
Battery capacity in EVs is measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), and the weight of a battery pack generally increases with capacity. While larger batteries provide extended range, the weight they add to the vehicle begins to offset the efficiency gains.
-
As battery capacity increases beyond a certain point (typically 100 kWh), the added weight causes diminishing returns on performance. This happens because:
More power is required to maintain the same level of performance: The motor works harder to move the heavier battery, consuming more energy without proportionally improving acceleration or top speed.
Additional strain on the motor: Heavier vehicles put more strain on the electric motor and drivetrain, requiring the vehicle’s motor to draw more power from the battery, which leads to faster depletion and decreased range.
-
When battery capacity exceeds 100 kWh, the added battery weight (around 1,500 pounds) significantly increases the vehicle’s total weight, pushing the vehicle toward or beyond the 7,000-pound range where efficiency declines. The increased weight requires more energy to move, so the benefit of extra range is diminished by the higher energy required to move the heavier battery.
-
Adding more power (in terms of kW from the motor) increases performance but also increases energy consumption. A high-performance vehicle with a large motor can deliver strong acceleration, but it will drain the battery faster, especially in heavier vehicles.
-
A 300–350 kW motor is generally the upper limit for what is considered efficient in mainstream EVs. Larger motors (above 350 kW) provide more power and acceleration but consume more energy, especially in heavier vehicles. For daily driving, this excess power rarely translates into usable range, resulting in reduced efficiency.
In heavier vehicles (over 6,000 pounds), larger motors are needed to maintain acceptable acceleration, but the energy consumption rises quickly, making the vehicle less efficient overall. Power in an electric vehicle (EV) is directly related to the battery capacity, motor output, and how these factors interact with the vehicle’s weight. When discussing tipping points for weight and battery capacity in relation to efficiency, the power dynamics of the vehicle are also affected.
-
The tipping point occurs when the increase in motor power leads to a disproportionate increase in energy consumption. At this point, the benefits of increased motor power—such as faster acceleration and higher performance—are outweighed by the much higher energy demand, which negatively impacts range and overall efficiency:
200 kW motor: 0.25 kWh/mile (baseline, efficient)
300 kW motor: 0.33 kWh/mile (+33.2% increase in energy consumption)
400 kW motor: 0.44 kWh/mile (+77.6% increase in energy consumption)
This shows that even though motor power has only doubled (from 200 kW to 400 kW), the energy consumption per mile has increased by 77.6%, highlighting the diminishing returns on efficiency.
-
The power-to-weight ratio is a critical metric that influences vehicle performance. A higher power-to-weight ratio results in better acceleration and overall performance. However, as vehicle weight increases due to additional battery capacity or heavier components, the power-to-weight ratio decreases unless the motor power is increased.
-
Maintaining this balance between weight, motor power, battery capacity, and energy consumption ensures that the electric vehicle delivers strong performance while maximizing range and efficiency. Vehicles designed with these metrics in mind offer the best combination of cost-effectiveness, environmental benefits, and practicality for everyday use. Learn about our ESG policy.
Our Process
Advancing Sustainable Innovation
By focusing on efficiency, we become more resilient.
-
At Alpha Motor, technologies like CAD (Computer-Aided Design), CAE (Computer-Aided Engineering), and virtual validation streamline complex engineering tasks at an industrial scale. As a result, Alpha Motor accelerates quality vehicle commercialization with greater capital efficiency than traditional methods.
-
Alpha Motor’s digital development reduces waste by eliminating resource-intensive trial-and-error cycles, enhancing efficiency in both development and manufacturing. The result is a more sustainable production process with reduced environmental impact and improved resource utilization.
-
Alpha Motor’s digitalization of manufacturing enables precision control, driving efficiency and quality standardization. It enables flexibility in production across different vehicle models and accelerates time-to-market. These efficiencies translate into cost savings, higher-quality vehicles, and scalable production capabilities.
-
Alpha Motor uses virtual validation to ensure vehicles meet safety, compliance, and performance standards early in development, reducing risks and improving reliability. Standardized digital processes enhance product quality, while advanced simulations test real-world scenarios, accelerating time-to-market. Feedback loops from digital platforms drive continuous improvement and ensure vehicles align with consumer needs.
-
At Alpha Motor, digital development is an advanced engineering process designed to streamline production. It is used to test and validate safety, performance, and manufacturing feasibility. This data guides all manufacturing processes, from CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining and stamping to assembly, painting, and quality control. It also supports marketing by providing accurate visuals that align products with consumer expectations. By connecting design, manufacturing, and consumer feedback, digital development enhances efficiency and enables high-quality production.
-
Alpha Motor’s digital strategies focus on process optimization and streamlining the standardization of quality. This enhances manufacturing efficiency and supports scalable, cost-effective production.
EV Charging Options
Charger Types
Power, Cost, and Connectors
-
Voltage: 120V (AC)
Power Output: 1.2 - 1.9 kW
Range per Hour: 3–5 miles
Cost per Mile: $0.04 - $0.05
Common Location: Residential
Connector Type: J1772
-
Voltage: 240V (AC)
Power Output: 3.3 - 19.2 kW
Range per Hour: 10–60 miles
Cost per Mile: $0.03 - $0.05
Common Location: Residential, Commercial
Connector Type: J1772, NACS
-
Voltage: 400V - 800V (DC)
Power Output: 50 - 350 kW
Range per Hour: 150–200 miles in 30 minutes
Cost per Mile: $0.15 - $0.30
Common Location: Commercial, Public
Connector Type: CCS Combo, NACS
-
Voltage: 800V - 1000V (DC)
Power Output: 350+ kW
Range per Hour: 200+ miles in 30 minutes
Cost per Mile: $0.25 - $0.35
Common Location: Commercial, Public
Connector Type: CCS Combo, NACS
-
Voltage: 120V - 1000V (AC, DC)
Power Output: Up to 350 kW
Range per Hour: 150–200 miles in 15 minutes
Cost per Mile: $0.04 - $0.35
Common Location: Residential, Commercial, Public
Connector Type: NACS (AC for L1/L2, DC for Fast Charging)
Key EV Metrics
Formulas and Definitions
-
Formula: Battery Capacity ÷ Energy Consumption
Key Factors: battery size, efficiency
Factors that Drive EV Range
Battery Capacity (Wh or kWh): The amount of energy the battery can store. Larger batteries provide more range.
Energy Efficiency: The vehicle's ability to convert energy from the battery into motion efficiently. Factors like aerodynamics, weight, and drivetrain efficiency contribute to energy efficiency.
Vehicle Mass (m): The total weight of the vehicle, including passengers and cargo. Heavier vehicles require more energy to move, reducing range.
Drag Coefficient (C_d): A measure of the vehicle’s aerodynamic drag. Lower drag coefficients improve efficiency and extend range.
Frontal Area (A): The area of the vehicle facing the wind. A larger frontal area increases air resistance and decreases range, especially at higher speeds.
Regenerative Braking: The ability to recover energy during braking and convert it back to the battery. Efficient systems help extend range.
Drivetrain Efficiency (η): The efficiency of the powertrain in converting electrical energy into motion. A higher efficiency means less energy is lost in the drivetrain, contributing to longer range.
Driving Style: Aggressive driving with rapid acceleration and hard braking reduces range, while smooth driving improves it.
Average Speed (V): Higher speeds increase aerodynamic drag, which increases energy consumption and reduces range.
Battery Health: The condition of the battery affects its ability to hold and release energy. As batteries age, their capacity and ability to provide range decrease.
Temperature and HVAC Use: Extreme temperatures require more energy to heat or cool the cabin, reducing range. Battery efficiency can also drop in very cold or very hot conditions.
Tire Pressure and Type: Properly inflated tires reduce rolling resistance, improving range. Tire type also plays a role, as performance tires have higher rolling resistance.
Drive Mode: Different driving modes (e.g., Eco, Normal, Sport) optimize energy use for various driving conditions. Eco mode prioritizes range by limiting acceleration and adjusting throttle sensitivity.
Auxiliary Loads (P_a): Power consumption from onboard electronics, HVAC systems, lighting, and other accessories reduces the available energy for driving, thus decreasing range.
-
Formula: Motor Power (kW) × 1.341
Key Factors: motor output, inverter performance
Torque, the motor's rotational force, is converted to horsepower for a more consumer-friendly measurement that also incorporates rotational speed, giving a clearer understanding of overall performance.
-
Formula: (Torque × Axle Ratio × Drivetrain Efficiency) ÷ 9.81
Key Factors: torque, drivetrain, cooling, structure
-
Formula: Range ÷ Battery Capacity
Key Factors: aerodynamics, weight, drivetrain losses
-
Formula: 100 ÷ Efficiency (mi/kWh) or Battery Capacity ÷ Range
Key Factors: driving conditions, vehicle load, speed
Factors That Drive Energy Consumption
Driving Conditions: Hilly terrain, rough roads, and extreme weather increase energy usage by requiring more power for movement or temperature control.
Vehicle Load: Heavier loads require more energy to move, increasing consumption.
Speed: Higher speeds increase energy consumption due to aerodynamic drag and rolling resistance.
Driving Style: Aggressive driving (rapid acceleration and hard braking) raises energy consumption.
Temperature Regulation: HVAC systems use extra power in hot or cold climates, reducing energy efficiency.
Aerodynamics: Poor aerodynamics increases energy consumption due to greater air resistance.
Tire Pressure and Type: Under-inflated or performance tires increase rolling resistance, raising energy use.
Regenerative Braking: Effective regenerative braking recovers energy, reducing overall consumption.
Vehicle Design: Heavier vehicles and less efficient drivetrains consume more energy; optimized designs improve efficiency.
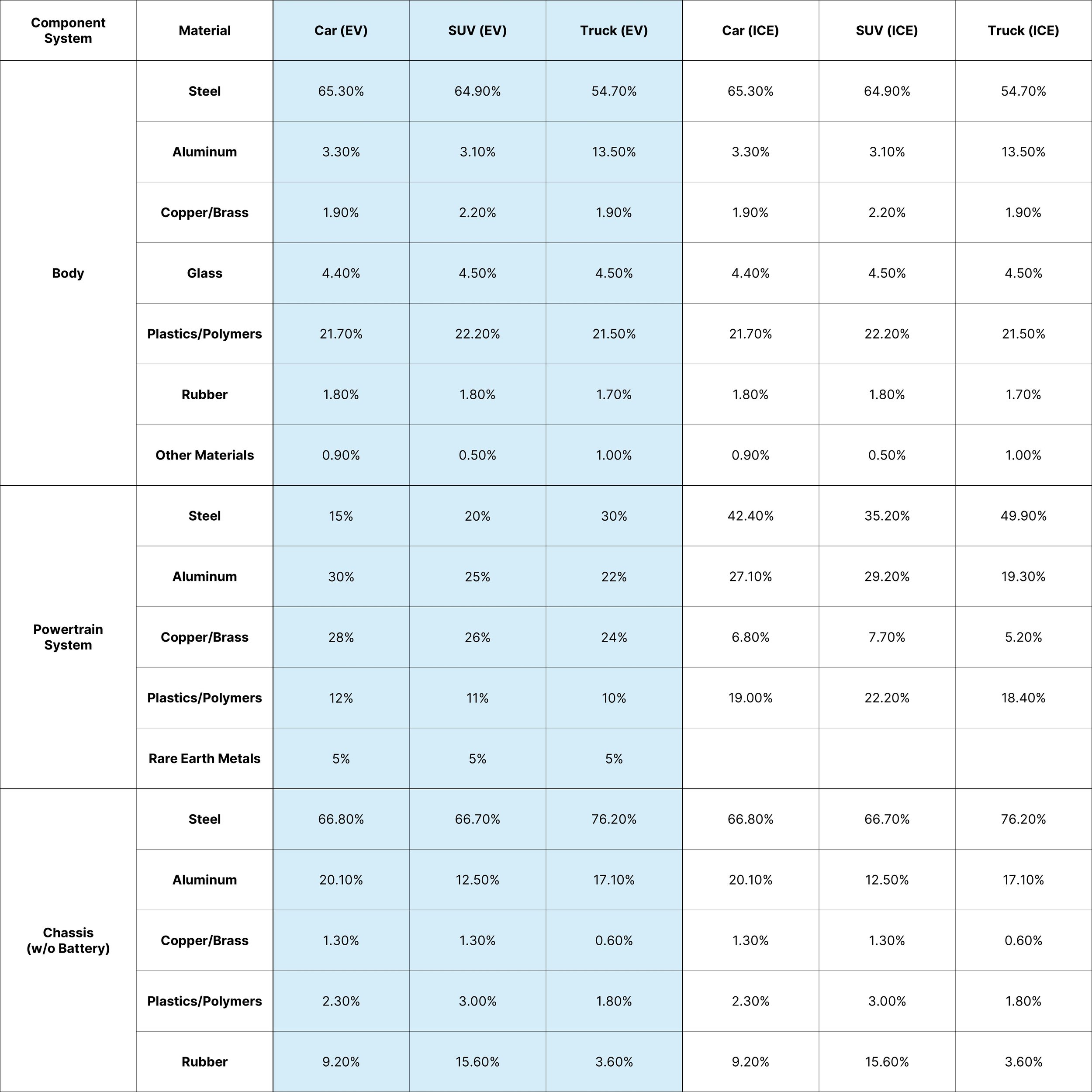
Vehicle Material Composition
Material Optimization Metrics
EV vs. ICE Material Breakdown
Material Optimization FAQ
-
EVs can utilize lighter materials because they don't require heavy internal combustion engines and transmissions, allowing for designs that offset battery weight and improve efficiency.
EVs have approximately 20 moving parts in their drivetrains, compared to over 2,000 in gasoline-powered vehicles, allowing for a focus on lightweight structural materials.
-
Lower weight reduces energy consumption, improves acceleration and handling, decreases rolling resistance, and allows for larger-diameter wheels that enhance aerodynamics and efficiency.
-
Carbon fiber is complex to manufacture for mass-market EVs, so cost-effective alternatives like aluminum, high-strength steel, and reinforced composites are used to balance weight savings and affordability.
-
EVs integrate battery packs into the vehicle's floor, lowering the center of gravity to enhance stability and handling, while eliminating the need for heavy engines and transmissions, allowing for the use of lighter materials to improve efficiency.
-
A multi-material approach is used in manufacturing EVs, combining high-strength steel, aluminum for lightweight panels, and composite plastics for non-structural parts to optimize efficiency.
-
Plastics make up 10% of a vehicle’s weight but 50% of its volume, significantly improving fuel efficiency.
The amount of plastic and polymer composites in vehicles has increased 18% over the past decade.
Mid-size EVs contain 45% more plastic than similar fuel-powered vehicles.
Thermoplastics resist heat and are used in battery compartments to improve cooling and extend lifespan.
Advanced plastics, such as polypropylene, are being developed to meet evolving EV manufacturing needs.
Recycling efforts are advancing to manage plastics at the end of an EV’s lifecycle.
The global EV plastics market is projected to grow rapidly, with a compound annual growth rate of 20-28%.
-
Easier and Faster Repairs: Plastic body panels and components can be molded into shape and replaced more easily than metal parts, reducing repair time and labor costs.
Lower Repair Costs: Unlike metal, plastic parts do not require expensive welding or refinishing processes, making replacements more affordable.
Corrosion Resistance: Plastics do not rust like steel or aluminum, increasing the longevity of components and reducing the need for replacements due to corrosion damage.
Lightweight Components: Plastics contribute to overall weight reduction, allowing for easier handling and installation of replacement parts.
Improved Impact Absorption: Thermoplastics and reinforced composites can flex upon impact, reducing damage severity and lowering the likelihood of needing full panel replacements.
Modular Design Compatibility: Plastic components are commonly used in manufacturing modular sections, allowing for easier part swaps without affecting the entire vehicle structure.
Simplified Manufacturing: Plastics can be easily mass-produced through injection molding, ensuring consistent part availability and reducing lead times for replacements.
-
Thermal Management: Plastics help regulate battery temperature by acting as insulators, reducing the risk of overheating and improving overall battery efficiency.
Lightweight Protection: Plastic battery enclosures provide strong yet lightweight protection, reducing overall vehicle weight and extending driving range.
Corrosion Resistance: Unlike metal casings, plastic housings do not corrode, improving the longevity and durability of battery components.
Design Flexibility: Plastics allow for complex, customizable battery housing designs that optimize space utilization and integrate seamlessly with vehicle structures.
Simplified Manufacturing: Injection-molded plastic battery components allow for precise, large-scale production, reducing costs and improving consistency in battery system assembly.
Survey
We Value Your Feedback
Your input is essential to our improvement.